
- Mac utility disco mac os x#
- Mac utility disco full#
- Mac utility disco verification#
- Mac utility disco software#
- Mac utility disco free#
The only solution must then be in the hdiutil command tool, despite its earlier warning that “hdiutil resize cannot resize filesystems other than HFS+ and its variants.” Thankfully, klanomath has worked out a solution here which is quite elaborate but appears to work on High Sierra and Mojave, with both regular and sparse disk images. It’s worth pointing out that if you repeated this but made the format of the disk image HFS+, resizing works absolutely fine. You can try changing the size of its container by repartitioning the image, but as the total size of containers can’t exceed the size of the disk image, that also gets you nowhere. You can try mounting the image and then resizing it: all that does is change the text in the error message.
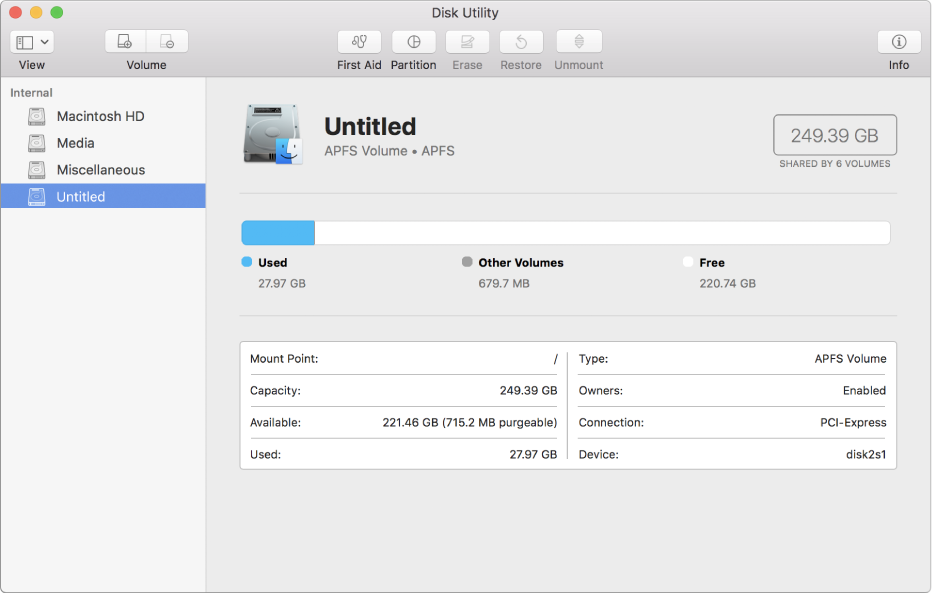
There’s no workaround in the Disk Utility app. You won’t even get as far as being invited to enter a new size, as Disk Utility comes straight back with an error. Now, follow Apple’s instructions for resizing that disk image using the Resize… command in the Images menu. To stop that, simply select your internal disk at the left, and it should behave more normally again. This is likely to provoke another lesser bug in Disk Utility: it will now start showing bursts of the spinning beachball and be sluggish in response. Once it’s created, eject your new disk image. You can make its image format anything you like, including a standard read/write disk image or either of the sparse options. Use Disk Utility’s File/New/Blank Image… menu command to create a new disk image, setting its format to APFS, and its size to something reasonable like 100 MB.
Mac utility disco full#
And I believe that this has been the case since the first full release of APFS in macOS High Sierra eighteen months ago. But if you create a disk image in APFS format, Disk Utility has a problem: it can’t change its size. Most users prefer to create and maintain them in Disk Utility, as the command tool hdiutil which handles them is so complex.
Mac utility disco software#
In OS X El Capitan, Disk Utility has a different user interface and lost the abilities to repair permissions due to obsolescence, create and manage disks formatted as RAID, burn discs, and multi-pass format internal solid-state drives and encrypted external drives.Disk Images are a popular way to deliver software and a great deal more.
Mac utility disco mac os x#
Mac OS X Leopard added the ability to create, resize, and delete disk partitions without erasing them, a feature known as live partitioning. Further changes introduced in Mac OS X Tiger, specifically version 10.4.3, allowed Disk Utility to be used to verify the file structure of the current boot drive. The ability to "zero" all data (multi-pass formatting) on a disk was not added until Mac OS X 10.2.3. Disk Copy was used for creating and mounting disk image files whereas Disk Utility was used for formatting, partitioning, verifying, and repairing file structures. Another application called Drive Setup was used for drive formatting and partitioning and the application Disk Copy was used for working with disk images.īefore Mac OS X Panther, the functionality of Disk Utility was spread across two applications: Disk Copy and Disk Utility.
Mac utility disco verification#
In the classic Mac OS, similar functionality to the verification features of Disk Utility could be found in the Disk First Aid application. It is also possible to create and manage RAM disk images by using hdiutil and diskutil in terminal. status of a hard diskĭisk Utility functions may also be accessed from the macOS command line with the diskutil and hdiutil commands.
Mac utility disco free#

Verifying a disk's integrity, and repairing it if the disk is damaged (this will work for both Mac compatible format partitions and for FAT32 partitions with Microsoft Windows installed).Mounting, unmounting and ejecting disk volumes (including both hard disks, removable media, and disk volume images).Creation, conversion, backup, compression, and encryption of logical volume images from a wide range of formats read by Disk Utility to.The functions currently supported by Disk Utility include:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
